 |
This is the case of a deadly female bite. The bite of a female black widow spider CAN BE lethal, though mostly to young children or senior adults. However, today’s modern treatments make the bite of this kind of spiders less dangerous.
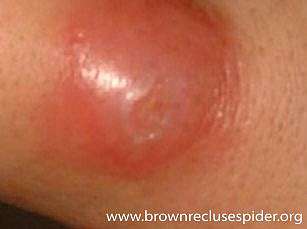
The bite does not cause instant pain, though it may turn quite painful within few hours. At first, it feels as if we were injured by a pin. |
But quickly, the venom runs and spreads through the veins, thus attacking the nervous system and causing the victim to develop certain symptoms such as swelling, reddening, nausea, stomachaches, muscular spasms, thorax cramps, abdomen and leg cramps, as well as contractions and deep pain.
Eventually, the venom strikes the nervous terminals, making it hard to breathe and swallow. The symptoms aggravate if the patient does not receive proper treatment/care : chills, sweating, convulsions, deep nausea, headaches, fever and paralysis. However, most cases do not grow so severe.
In the case of pregnant women, the bite of the Black Widow Spider may cause contractions and premature delivery. The victim must be urgently carried away to an emergency room for immediate treatment.
Black widow spiders belong to the Latrodectus genus, and there are several species found worldwide. The most well-known species is the southern black widow (Latrodectus mactans), found in the United States.
Female black widow spiders are typically larger than males, measuring about 1.5 inches (3.8 cm) in length, including their legs. They are easily identifiable by their shiny black bodies with a characteristic red hourglass-shaped marking on the underside of their abdomen. However, the hourglass marking may be absent or faint in some species or individuals.
Male black widow spiders are smaller and less venomous than females. They have longer, thinner legs and a smaller body size. They often have yellow or red bands or spots on their abdomen instead of the hourglass marking.
Black widows are known for their distinctive web spinning behavior. They create irregular, tangled webs close to the ground, typically in dark, sheltered areas. The webs are strong and sticky, designed to ensnare insects and other small prey.
Black widow spiders are not aggressive and usually bite only in self-defense when they feel threatened or disturbed. They may bite if they are accidentally squeezed or pressed against the skin, such as when putting on clothes or shoes without checking for their presence.
Male black widows rarely bite humans since they are less venomous and their fangs are not long or strong enough to penetrate human skin effectively.
The venom of black widow spiders is considered a neurotoxin, affecting the nervous system. It acts by interfering with the transmission of nerve impulses, leading to the symptoms associated with a black widow bite.
While black widow spider bites can be painful and cause significant discomfort, deaths from black widow bites are rare, especially with modern medical treatments. Most healthy individuals recover fully with appropriate medical care.
Black widow spiders have a remarkable lifespan compared to other spiders. Females can live up to three years, while males typically have a shorter lifespan of several months.
Black widow spiders are beneficial to ecosystems as they help control populations of insects and other small arthropods. They play a role in maintaining the balance of natural habitats.
See also : more about bite symptoms and first aid procedures in the link on the left-hand corner of the site.
See also : pictures of bites are available on the links appearing in the menu.
« Back to brown recluse spider home
